|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Netlist Analyzer and ECO toolGates-on-the-Fly (GOF) graphically analyzes and edits large Verilog netlists that have been generated from a synthesis or layout tool. Netlists sometimes require changes to either meet timing closure specifications, fix functional logic bugs, or to repartition a design. Using GOF, you can easily find and view specific logic cones in your design on a schematic to visualize just the paths you need to see without unnecessary clutter. GOF also simplifies mapping from RTL level constructs to their gate-level equivalents, so that you can pinpoint the locations where changes need to be made. GOF's ECO mode supports both graphical and script-based editing features for tracking ECO changes. Metal-only ECO operations are also supported with an automatic spare gates flow.
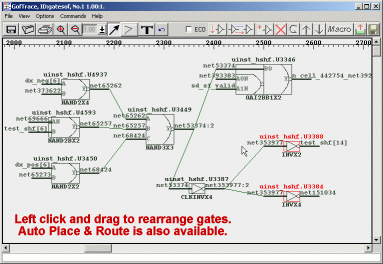
GOF has four main parts: a netlist browser (GofViewer), a schematic viewer (GofTrace), a netlist editor (GofECO), and a scripting program for automating changes (GofCall). You can also debug a design using one of SynaptiCAD's Waveform Viewers to annotate GofTrace schematics with state information from a waveform file (either from a simulation debug session in progress or from a VCD file created during an earlier simulation of the design). Below is a typical design flow using GOF: (1) Locate Sections of interest in the design in GofViewerGofViewer displays a netlist as a hierarchical tree of module instances with an associated text window. This is the first window opened after launching GOF from the command line. From this window, the design can be quickly explored by double clicking on the tree and viewing the code. Use the right click context menus and/or double click on objects to quickly find related information such as the drivers and loads of a particular net. GOF is optimized to handle very large netlists, so it only loads the module that you are looking at.
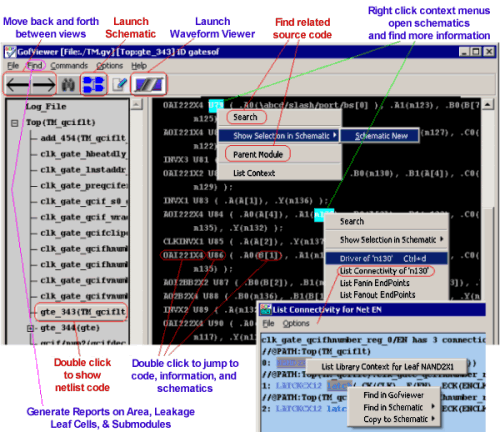
(2) Investigate gates using GofTrace schematic windowsOnce a netlist is loaded, you can view sections of the design as a schematic using a GofTrace schematic window. GofTrace allows you to quickly display only the portion of logic that you are interested in by focusing on tracing just the fan in/out of a particular path, unlike other schematic tools which force a fixed placement of the gates that makes it difficult to rearrange the gates to visualize just the area of interest.
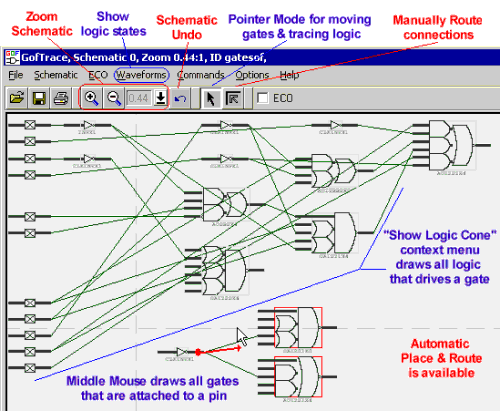
Initially a schematic is drawn with straight wires between connections so that you can quickly view the circuit and get an idea of the gates and buffers that have been added by the synthesis tool. However, the nets can then be automatically routed using the Place & Route menus or manually routed with the Line Select Mode to produce quality documentation.
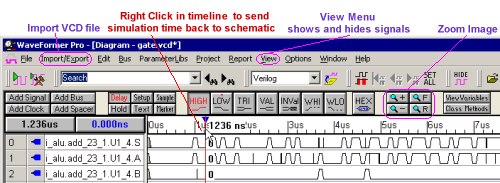
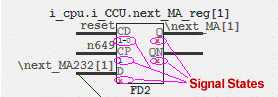
Using one of SynaptiCAD's waveform viewers, you can view waveforms from a simulation or a waveform file (e.g. a VCD file) and also show specific logic states annotated on GOF schematic Windows. The schematic and the waveform displays are linked so that you can quickly display just the waveforms that match the nets of your schematic. You can also right click in the waveform window to send logic states at a particular simulation time back to the schematic.
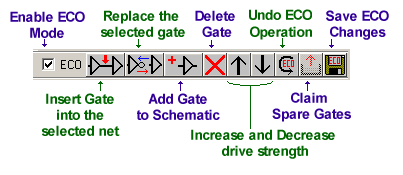
(3) Use GofECO to graphically edit the netlist gates and connectionsGofECO is a graphical method of changing a netlist. You can add, delete or replace gates. You can also add or delete connections between gates and adjust the drive strength of buffers. The schematic background changes color to indicate that the diagram is in ECO mode, and all ECO changes are displayed in a different color than the schematic gates and connections.
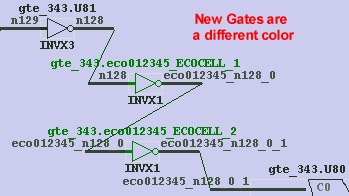
(4) Use GofCall for automatic ECOs and Checking the SchematicUsing GofCall's programming API, complicated ECOs can be performed with only a few lines of scripting code. The API lets the user focus on the logic changes, without having to specify all the details like adding hierarchical ports or naming new nets. The GofCall API statements can be entered through an Interactive Command window or executed using a batch file.
change_pin("u_spares/s0/A", "gte_344/U101/Y");
change_pin("u_spares/s0/B", "gte_344/U143/Y");
change_pin("gte_344/gte_con_reg/D", "u_spares/s0/Y");
Above is an example of a three line script that borrows a gate from the spare gate list and makes the connections needed to logically connect up the gate using the change_pin API call. The first line connects up the A input of u_spares.so to the Y output of gte_344.U101, the second line connects up the B input of u_spares.so to the Y output of gte_344.U143, and the third line connects up the D input of gte_344.gte_con_reg to the Y output of u_spares.s0. GofCall will automatically take care of all the tedious aspects of naming nets and creating ports during the connection process. GOF Features
Evaluate and Purchase Gates-on-the-Fly
|
|
|
